Cell Organelle with their functions, structures and discoverers
INTRODUCTION TO CELL ORGANELLES
As we know that every living organism is composed of Cell and inside of these cells there is the presence of structures that helps it to perform various functions such as growth, digestion, immunity, etc.. which keeps the entire system within the cell active. These structures are together known as Cell Organelles.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
- Cell Organelles definition
- List of Cell Organelles
- Nucleus
- Ribosomes
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Golgi Apparatus
- Centrosome and Centriole
- Plastids
- Mitochondria
- Plasma Membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Microbodies
- Vacuoles
- Lysosomes
- Cytoskeleton
- Importance of Cell Organelles
- Frequently asked questions related to cell organelles with their answers.
CELL ORGANELLES DEFINITION
An Organelle is a specialized structure or compartment that has specific functions to do within the cell.
In other words, Organelles are the subunit of cells that have tasks to do inside them. Among all the Organelles present in the cell, some of the major organelles are Nucleus, mitochondria, Ribosomes.
The Cell Organelles are classified into 3 types based on the number of membranes they have:-
- Organelles without a membrane - Various Cell Organelles such as Cytoskeleton, Centriole, Ribosomes, etc.. are non- bounded with any membrane. They are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Organelles with single membrane - Some Cell Organelles like Golgi apparatus, Lysosome, Vacuole, etc.. are covered by a single membrane. They only exist in eukaryotic cells.
- Double membrane-bound Organelles Nucleus, Chloroplast, Mitochondria are the Organelles bounded by double membranes. They are present in eukaryotic cells.
LIST OF CELL ORGANELLES
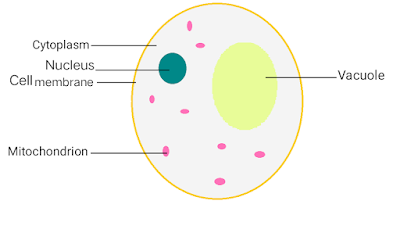
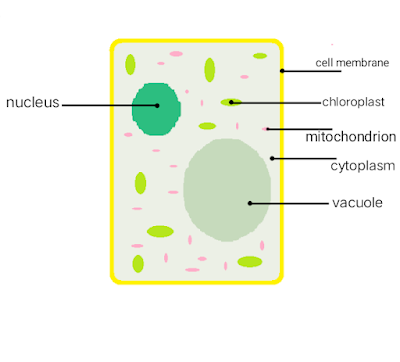
Nucleus
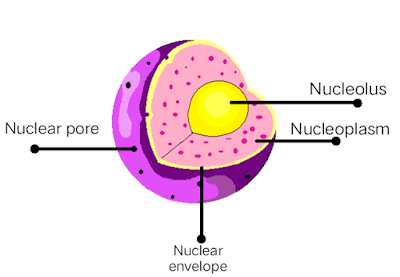
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle present in the center of eukaryotic cells that consist of genetic materials such as DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of cell inside it. It is known as the “control center” of cells as it controls every activity happening inside the cell and also keeps the hereditary information of the cell.
The basic Nucleus structure is made up of 5 main parts - Nuclear envelope, Nucleoplasm, Chromatin, Chromosomes, and nucleolus. It is spherical and is surrounded by a nuclear membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. The nucleus is the largest organelle in the cell covering about 10% of the whole cell volume.
The nucleolus is a tiny spherical structure present inside the nucleus that helps in the transcribing and processing of Ribosomal RNA (Ribonucleic acid).
Who discovered the nucleus?
Nucleus was discovered by Robert Brown in 1831.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are non-membrane-bound Organelle present in both Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. Ribosomes are composed of Proteins and Ribosomal RNA (Ribonucleic acid). Ribosomes are the place where the process of manufacturing proteins for the cell called Protein synthesis takes place. This process is very important for the survival of cells.
Ribosomes consist of sections inside them that are divided into 2 parts, collectively called subunits, one consists of mRNA (Messenger RNA) while the other consists of amino acid. mRNA is a single standard molecule that helps transport the genetic code from DNA - (cell's Nucleus) to the Ribosomes while the Amino acid is utilized in the process of proteins synthesis. Ribosomes either can be floating on the cytoplasm of the cell or can be on the membrane surroundings of the Endoplasmic Reticulum.
Who discovered Ribosomes?
Ribosomes were discovered by
George Palade in 1955.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a large membranous structure that starts from the nucleus and spreads throughout the Cytoplasm of the cell. It consists of continuous foldings or a network of Cisternae (series of flattened and curved membranes) that are held together by the Cytoskeleton. It is present only in Eukaryotic cells.
The ER consists of two subunits, They are:-
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) - The presence of Ribosomes on the surface of RER makes it rough and uneven, therefore the name “Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum”. RER is made up of vesicles, cisternae & tubules and functions in producing Protein for the cells that are done by Ribosomes, present on its surface.
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) - The surface of SER does not contain Ribosomes or any substance on it making it smooth, therefore the name is “Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum”. It is composed of tubules and cisternae. They produce lipids, steroids, phospholipids (lipids containing phosphate).
Who discovered Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Endoplasmic Reticulum was discovered by
Albert Claude and Keith R. Porter in 1953.
Golgi Apparatus
Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound Organelle also known as Golgi Complex, Golgi body or only Golgi that is located in the Cytoplasm of the cell near the Nucleus and alongside Endoplasmic Reticulum.
It is composed of a series of cisternae (flattened and curved membranes). It is found in Eukaryotic cells.
It receives the lipids and proteins from the Endoplasmic Reticulum where the proteins are made by Ribosomes present in RER through the process of protein synthesis and the lipids are made by lipid synthesis that happens in SER. The Golgi apparatus then packages and transports them to different parts of the cell.
It is named after the person who discovered it.
Who discovered Golgi Apparatus?
Golgi apparatus is discovered in 1898 by
 |
| Golgi Apparatus Diagram |
Centrosome and Centriole
The centrosome is a non-membrane-bound Organelle present in the cytoplasm, near the nucleus of the animal cell. The Centrosome is responsible for organizing the microtubules (made of proteins) in the process of mitosis, therefore it is also known as the microtubule-organizing center of the cell. It also plays a major role in Cell division and helps in providing the structure and shape to the cell.
The Centrosomes consist of two structures tied to each other and are known as Centrioles, the two centrioles are namely - Mother Centriole and Daughter Centriole. The centrioles are cylindrical and are composed of microtubules that are made of a protein called - Tubulin. They consist of 9 pairs of microtubule triplets (3 microtubules in each pair) grouped and arranged circularly, making them cylindrical. Centrioles help in making the spindle fibers that further form the mitotic spindle that helps in the process of mitosis.
Who discovered Centrosomes?
The Centrosomes were discovered in 1876 by Van Beneden.
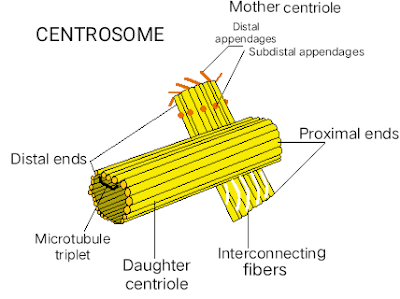 |
| Diagram of Centrosome |
Plastids
Plastid is a membrane-bound organelle that is generally found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are the organelle in the cell which is responsible for the manufacturing (Photosynthesis) as well as the storage of food, starch, oils, proteins, etc. Plastids are generally of 3 types depending on the pigment or color.
They are -
• Chloroplast - Chloroplast is a double membrane-bound organelle that is generally spherical, oval, or disc-shaped. It contains a green pigment called chlorophyll inside it that absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy which is utilized in the process of photosynthesis, chlorophyll is also responsible for the green color in plants and leaves. Chloroplast contains two membranes, inner and outer membrane with a space left between them. The inner membrane contains stroma (colorless and dense fluid) and structures known as thylakoids (containing chlorophyll) inside it. Thylakoids are arranged in stacks. Chloroplast is found in the mesophyll of leaves. Chloroplast was discovered by Hugo Von Mohl in 1837.
• Chromoplast - chromoplast is present in roots, flowers, fruits, and some certain leaves as it gives them different colors including red, yellow, orange, etc. This happens due to the presence of Carotenoid pigment (producing bright colors) inside it as they lack chlorophyll. The production and storage of Carotenoid pigments are done by the chromoplast itself and they are also included in the dispersal of seeds and pollination.
• Leucoplast - leucoplast are found in the non-photosynthetic tissues of the plant as they are non-pigmented (colourless) and non-photosynthetic (lack of photosynthetic pigments) organelle present in the plant cell. Leucoplast are of three types, they are:
• Amyloplasts - functions in the storage of starch.
• Proteinplasts - functions in the storage of
protein.
• Elaioplasts - functions in the storage of fats, oils, and lipids.
The leucoplast was discovered in 1883 by Andreas Franz Wilhelm Schimper who also
invented the name Plastids.
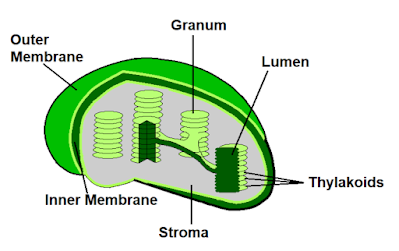 |
| Plastids diagram |
Mitochondria
Mitochondria is a double membrane-bound organelle located in the cytoplasm of Eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria are considered as the powerhouse of the cell as it helps in the process of cellular respiration and is also the production center of the energy-rich molecule, ATP (Adenosine triphosphate), which is also known as the energy currency of the cell. ATP is utilized to store and withdraw energy when needed for the cellular parts to function. Mitochondria also manage cellular metabolism.
Mitochondria contain an outer & an inner membrane with an intermembranous space left between them. The inner mitochondrial membrane consists of foldings made of cristae as well as the matrix (that helps in the synthesis/production of ATP) inside it.
The inner membrane is non-permeable while the outer membrane is permeable for specific substances (selectively permeable). The outer membrane also surrounds the whole mitochondrion. Mitochondria is generally an oval or round-shaped organelle.
Who discovered Mitochondria?
Plasma membrane
Plasma membrane or Cell membrane can be considered as separation of internal cells From the outer cellular environment. It is selectively permeable i.e. can pass some specific substances in and out of the cell. The plasma membrane is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and functions similarly in each of them. The plasma membrane functions as a protection to the cell provide it shape, strength, maintaining a fixed environment, helps in transporting substances in and out by (active & passive transport).
The plasma membrane is made up of two macromolecules, membrane proteins (integral and peripheral) and lipids (phospholipids, glycolipids & cholesterol) that make up the lipid bilayer. It is also considered a fluid mosaic model as it consists of fluid i.e. lipid layers with proteins embedded on top of it which make the structure of the plasma membrane.
Who discovered the Plasma membrane?
Robert Hooke in 1665 examined the Plasma membrane and the scientists Singer and Nicolson made the fluid mosaic model in 1972.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a jelly-like fluid or liquid present inside a cell that carries all the cell's materials and organelles (except the nucleus) floating or embedded in it. It can be found on both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, every cell indeed. The cytoplasm is one of the most necessary organelles in the cell as it helps the cell in growth, replication, cell expansion, etc.. as well as all the organelles, are embedded in the cytoplasm. It also helps in giving the shape to the particular cell.
The cytoplasm is made up of proteins, water, and salts where it's 80% of water and the rest of salts and proteins. It also includes cytosol (Cytoplasmic matrix) with it. The cytoplasm is of watercolor i.e. colorless.
Who discovered cytoplasm?
Rudolf von Kölliker in 1862 discovered the cytoplasm.
Microbodies
Microbodies are organelles in the cell bounded by a singular membrane that includes peroxisomes, glyoxysomes, hydrogenosomes, and glycosomes in their family. Microbodies contain enzymes and proteins that help in different chemical reactions in a cell such as the breakdown of fats, amino acids, and alcohol, etc. Also, they are responsible for the detoxification of peroxides.
Microbodies are smaller in size as compared to other organelles in a cell and are spherical. They are present in the cytosol of cytoplasm which is why they are also known as "cytosomes". It is a vesicular structure surrounded by a single membrane of a phospholipid bilayer and does not have its DNA.
Who discovered Microbodies?
Microbodies were discovered by Johannes Rhodin in 1954.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are the membrane-bound organelle present in plants, animals, fungal and bacterial cells. They are enclosed compartments filled with fluid (cell sap) inside it, vacuoles can also be considered as cell closets as they store foods and a variety of nutrients inside it as well as they also store waste products that prevent the cell from contamination. The waste is then dumped out of the cell with no harm to the vacuole or any part of the cell. Vacuoles help in maintaining water balance in plants and also help their organs to grow very quickly using water.
Vacuoles are covered by a membrane made up of phospholipids and proteins and are filled with the cell sap that is made of sugar, water, salts, and amino acid. It has no specific shape or size as its structure depends on the requirements of the cell. Sometimes it also takes a large shape in plant cells due to its functions that include water.
Who discovered Vacuoles?
Vacuoles were first discovered by Lazzaro Spallanzani in 1776 and named by Félix Dujardin in 1841
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelle present in the eukaryotic cells. Lysosomes are also known as the “suicide bags” of the cell as they consist of hydrolytic enzymes that help in the breakdown of cellular waste (unwanted materials) as well as when the cell is damaged, the released enzymes then digest their cell in a process known as apoptosis (programmed cell death) causing it to die/self destruct. The lysosomes help in the digestion of material in and outside of the cell. Lysosomes also contain different types of enzymes used for the breakdown of biomolecules.
Lysosomes are spherical in the shape and are bounded by a single membrane that protects the cell from the digestive enzymes that are harmful to the cell. The membrane is made with lipids and the enzymes are made with proteins that happen in RER. Apart from digestion lysosomes also help in different cellular processes like destroying viruses and bacterias etc.
Who discovered Lysosomes?
Christian de Duve discovered the lysosomes in 1955.
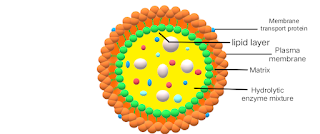 |
| Diagram of lysosomes |
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a continuous network of protein filaments or fibers present in the cytoplasm that extends from the nucleus to the Plasma/Cell membrane of the cell. The cytoskeleton is present in Eukaryotic cells and functions in giving shape and mechanical support to the cell. It also functions in the cell's internal organization, movement of various cell organelles and is also responsible for the locomotion of cells. The cytoskeleton is also known as the skeleton system of the cell as its network reaches every part of the cell.
The cytoskeleton is non-membranous organelles that are made up of three main components or fibers -
- Microtubules
- Actin filaments
- intermediate filaments
These components help the cytoskeleton to function and are capable of rapid growth and disassembly if required to the cell. The cytoskeleton is small as compared to other organelles.
Who discovered the Cytoskeleton?
Nikolai K. Koltsov in 1903 discovered the cytoskeleton
Importance of Cell Organelles
Cell Organelles have duties (functions) to do within the cell to keep it alive and working. They are of different types and have their structure and Functions to perform in a cell. Cell Organelles are important to the cell because a cell will not exist without its Organelles just like humans without organs (it'll be Nothing) life on earth will not exist, therefore they are so important for all living cells including humans, plants, animals, etc.. to survive.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Question
What are cell Organelles?
Answer - As we know that every living organism is composed of Cell and inside of these cells there is the presence of structures that helps it to perform various functions such as growth, digestion, immunity, etc.. which keeps the entire system within the cell active. These structures are together known as Cell Organelles.
Question
Which part of the cell contains Organelles?
Answer - Cytoplasm is the organelle where all the cell Organelles (except nucleus) and materials of the cell are present floating or embedded on it. It is a jelly-like fluid or liquid present inside the cell that is spread throughout the whole cell.
Question
Which cell Organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell?
Answer - Mitochondria is the organelle considered as the powerhouse of the cell as it helps in the process of cellular respiration and is also the production center of the oxygen-rich molecule, ATP (Adenosine triphosphate), which is also known as the energy currency of the cell.
Question
Why lysosomes are known as suicide bags?
Answer - Lysosomes are also known as the “suicide bags” of the cell as they consist of hydrolytic enzymes that help in the breakdown of cellular waste (unwanted materials) as well as when the cell is damaged, the released enzymes then digest their own cell in a process known as apoptosis (programmed cell death) causing it to die/self destruct.
Question
which cell organelle is involved in apoptosis?
Answer - Lysosomes are involved in the process of apoptosis, when the cell is damaged they digest on its own causing it to self-destruct or die.
Question
Which Organelle is the site of photosynthesis?
Answer - chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll inside it that absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy which is utilized in the process of photosynthesis.
Follow us on our social media.
Join :-
Become a contributor to our board on Pinterest
Get a free subscription to our space on Quora
Share and comment down below.






Very well done friend ..... It will help me alot for my exam .... nicely done 🙏🙌❤️😊 thanks
ReplyDeleteNice information...glad that you have intrest in these ....it is very informative and helpful for exam...those who are not going to coaching , this is just like very much helpful to them specially😊😊👍🏻✨✌️great job bro....🤟🤟🤩🤩
ReplyDeleteGreat work bro ❤
ReplyDeleteLoved it..
Very well organized and explained.
ReplyDelete