The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9
Cells
★ Scientist Robert Hooke in 1655 found cells for the first time during an observation while examining a dried section of cork tree with a crude light microscope, he observed small chambers and named them cells.
★ Cells are known as the structural and functional unit of life as all living organisms are composed of cells.
★ All the functions of organisms like growth, movement, digestion, immunity, etc are done by cells.
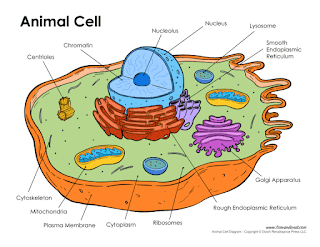
★ Cells contain different types of components like Cytoplasm, Mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, Centriole, Ribosomes, etc which help in the life of cells.
★ The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a double layer consisting of proteins and lipids surrounding the cell which separates cytoplasm (inner content of cell) from the external environment.
★ Cell groups with each other to form tissues and the tissues group together to form body organs like the brain, liver, heart, etc.
★ The organized or specialized structures within the living cell are called Organelles.
Example:- Lysosomes, Vacuoles, Plastids, etc.
★ The entire content of living cells including the nucleus and cytoplasm is called protoplasm.
★There are two kinds of organisms based on cells:-
1-Unicellular Organisms - consist of single cells and constitute whole organisms.
2-Multicellular Organisms - consist of more than one cell
FACT- WHITE BLOOD CELLS (WBC) AND RED BLOOD CELLS (RBC) CAN CHANGE THEIR SHAPES.
TYPES OF CELLS
The cells are of two types -
1) EUKARYOTIC
2) PROKARYOTIC
• The eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus while the prokaryotic does not.
• Examples of eukaryotic cells include-
Plants, animals, fungi, protozoa, algae (everything except prokaryotes).
• Prokaryotic are single-celled while the eukaryotic can be single or multicellular.
• Examples of prokaryotic cells include-
Bacteria and Archaea.
STRUCTURE OF CELL
The structure of cell consists of three parts:-
1-cell wall and cell membrane
2-Nucleus
3-cytoplasm, which is in between the cell membrane and nucleus.
Let us understand these components -
1- Cell wall and Cell membrane:-
★Cell wall - cell wall is the outermost layer in some type of cells, covering the cell or plasma membrane. For example- plant cells, algae, fungi, and bacteria.
★Functions of cell wall - it provides strength, rigidity, and structural support to a cell. It protects the cell from damage and gives it shape.
 |
| Image Source - Google | Image by - factsjustforkids.com |
★Cell membrane - cell membrane also known as the plasma membrane is a double layer of proteins and lipids surrounding the cell. It is present in all types of cells for example - animal cells, plant cells, etc.
★Functions of cell membrane - It provides protection, separate cytoplasm from the outside environment, transports nutrients inside the cell, and removes toxic substances which harm the cell, and many more.
|
★ Difference between the cell wall and cell membrane:-
Cell membrane
• it is present in every type of cell.
• it is made up of lipids and proteins.
• cell membrane is living.
• it is thin and flexible.
• cell membrane is selectively permeable.
• it changes the shape as needed.
• it protects the cell from the outside environment and also maintains the inner environment.
• Examples of cells with cell membranes are - humans, animals, plants, etc (all except the one with a cell wall).
Cell wall
• it is present only in the plant cell, algae, bacteria, and fungi.
• it is made up of cellulose.
• cell wall is non-living.
• it is thick tough and rigid.
• cell wall is freely permeable.
• it has a fixed shape.
• it protects the cell from the outer environment.
• examples of the cells with cell walls are - plant cells, algae, bacteria, and fungi.
2 - Nucleus:-
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle located in the center of the eukaryotic cells and is covered by a spherical enclosed membrane called the nuclear membrane. It acts as a controller or manager of cells and is considered the largest organelle in a cell with occupying about 10% of the whole cell.
Function- it comprises of the genetic material concerned with the transmission of hereditary traits from parents to the younger ones, stores DNA, most of the important cellular processes are done in the nucleus, it controls all the activities of cell-like growth, reproduction, etc.
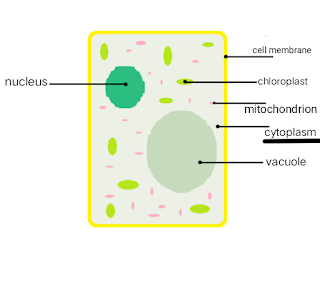
3 - Cytoplasm-
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that is filled between the nucleus and the cell membrane. It is composed of salt, water, and many organic molecules. Various cell organelles like mitochondria, ribosomes, chloroplast, Golgi apparatus, etc.. are present in the cytoplasm.
Function- It consists of enzymes that are important for the breakdown of waste materials inside the cell, it fills up the cell so that the Organelles remain in their position, assists the metabolic activities, various activities of the cell are done in the cytoplasm, it provides shape to the cell.
 |
| Cytoplasm inside a cell |



Great work
ReplyDeleteGreat brooooo
ReplyDeleteNice information
ReplyDeleteI found it helpful for my exams thx.
ReplyDeleteGreat bro well done it helped me alot
ReplyDelete